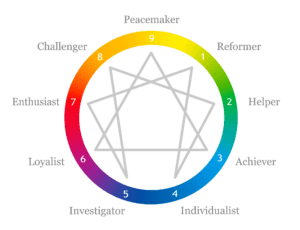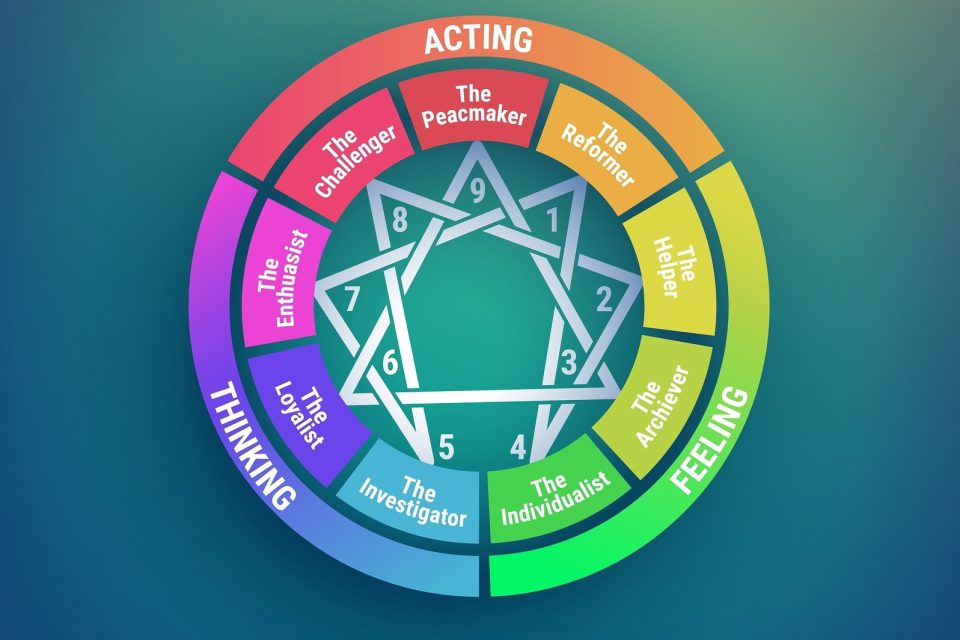
What is the Enneagram System?
The Enneagram is a Personality Typing System comprising nine different types. The nine types (or “enterotypes,” “ennea” means “nine”) are universally identified by the numbers 1 to 9.
While it’s uncertain whether your type is genetically determined, many believe it is already in place at birth.
People of a particular type have several characteristics in common, but they can be pretty different. Their level of mental health, among other things, can determine their appearance. Unhealthy (neurotic) people of a particular type can look quite different from healthy ones.
It is thought that everyone is considered to be one single type. However, individuals can have traits belonging to many styles.
Katherine Chernick Fauvre has proposed the Enneagram Tritype®, which consists of one Enneagram Type in each intelligence center. Although one of these three Enneagram Types is dominant, you use the other two types in your Tritype in a consistent and preferred order.
There are many tests to help you find your type, but it’s best to learn about each type and the triads and select the one you feel represents you the most. Often, the easiest way is to review the basic fear of each kind; the one that resonates with you best is likely your type.
Understanding the Enneagram Symbol
The symbol dates back about 2500 years. However, the actual date of its beginning or where exactly it started is unknown.
It is a coming together of the wisdom of many different spiritual traditions. Much of it has come from Christianity, Buddhism, Islam (especially Sufis), and Judaism.
It encompasses three central figures: the Circle, the Triangle, and the Hexad. Each of these figures symbolizes the three Laws of the Universe.
The Law of Three and Seven
The Enneagram symbol illustrates how the “Law of Three” and the “Law of Seven” function in tandem.
The Law of Three implies that every phenomenon results from three opposing forces.
The Law of Seven explains the development of processes. We use the number “7” because it is the law of octaves.
If you’re familiar with a musical scale, you’ll know that there are seven basic tones (do-re-me-fa-so-la-si), with the fundamental (do) naturally being repeated in playing a musical scale.

The Circle represents the Oneness of life and the container within which we live out the context of our lives.
It represents the Wholeness of humans before we were seemingly fragmented by ego and after we have become aware that we have never lost that Wholeness.

The Triangle represents the Law of Threes, which states that every phenomenon is composed of three separate sources: the Active, the Passive, and the Neutral.
Another is the concept of The Perceiver, the Act of Perceiving, and The Perceived.
The Hexad is a six-pointed figure that follows seven points from the beginning through six changes in momentum, then back to its origin, the seventh point.
The Hexad represents the Law of Seven, which considers the path of movement toward and away from anything in our world as not a straight line but periods along the journey of striving, failing, and striving again, a rising and falling of energies along the path.
The Enneagram Symbol is an overlay of the three elements that symbolizes a path to a fuller, more prosperous life,
To summarize, the Enneagram Symbol is a Triangle (Law of Three), a Hexad (Law of Seven), and a Circle (both as laws of unity).
Enneagram Fears
A lesser-known fact about the Enneagram is that it isn’t meant to be a system that merely identifies clusters of traits.
The Enneagram is a dynamic, growth-oriented inventory that aims to pinpoint one’s basic fears and motivations to facilitate personal growth through a specific trajectory.
Which traits you utilize – helpfulness, creativity, dutifulness, etc. – are manifestations of your primary fears. However, the behaviors you employ to escape your worries can be situational.
A type six may tap into their creative side to please a mentor – to avoid their primary fear of being without support or guidance – and consequently mistake themselves for a type four.
A type three may act dominant and assertive to progress professionally and mistake themselves for a type eight.
When judging our style based on behavior, we are at high risk of mistyping ourselves.
Just as cognitive functions explain the mental processes that drive each Myers-Briggs type’s behavior, the Enneagram’s basic fears identify the driving force between the nine types’ behaviors.
The best way to identify your type is to learn the basic fears for each Enneagram Type. The one that resonates the most with you is most likely your type.
You will see yourself in all the classes, but one will make you feel the most uncomfortable or embarrassed, and this is probably your type.
Enneagram Centers of Intelligence – The Triads
The nine Enneagram Types are further divided into three triads:
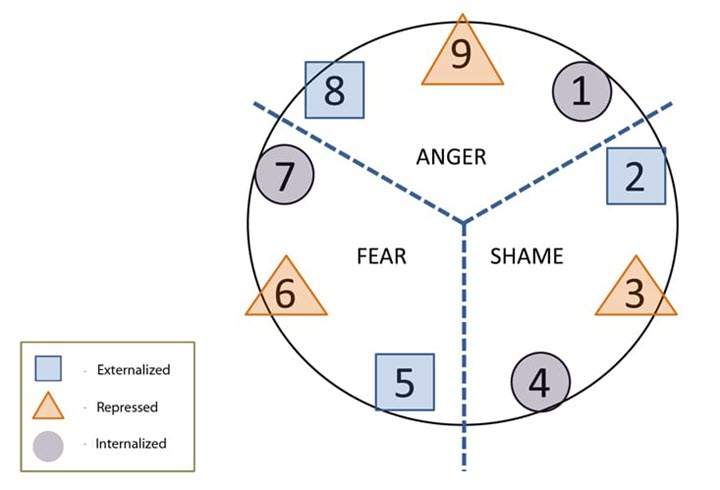
- Gut / Body / Instinctive – Emotion: Anger / Rage
- Heart / Feeling – Emotion: Shame
- Head / Thinging – Emotion: Fear
These triads or centers represent perception, processing, and expression modes: moving or sensing (kinesthetically), feeling, and thinking.
Each center’s function has its advantages and disadvantages—its positive uses and misuses—ways it helps us interpret and interact with the world around us and can steer us off course.
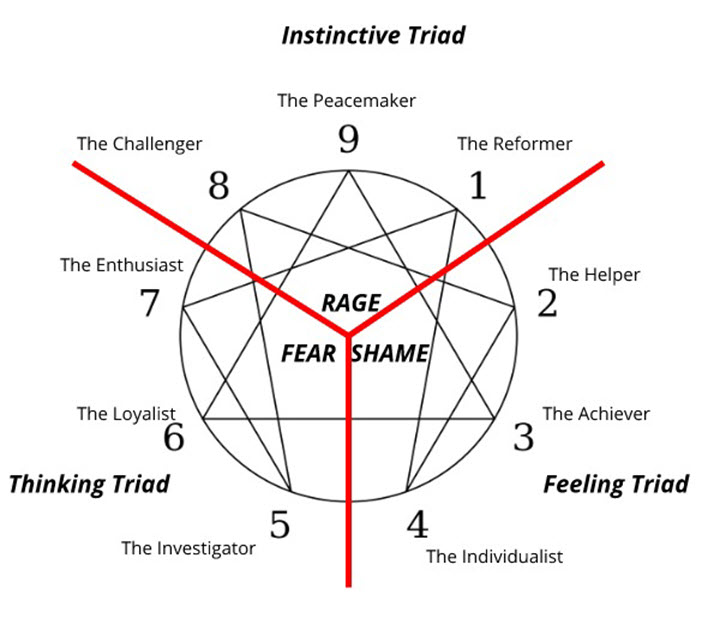
Again, depending on the type, these emotions are approached differently:
- Externalized
- Internalized
- Repressed
For example…
- Eight’s will Externalize their Anger.
- Two’s will Externalize their Shame.
- Five’s will Externalize their Fear.
The Gut / Body / Instinctive Center
The “body” center includes the “motor” center (Points 8, 9, and 1), which takes an active part in all physical movement, and the “instinctive center,” which corresponds to our instinctual functions.
When thought initiates movements within you, your motor center is activated.
An impulse from the motor, or gut, the center can be a solid guide to the right action, but misuse of the motor center can also lead to impulsive behavior or inertia.
The Heart / Feeling Center
The “heart” center or “emotional” center (Points 2, 3, and 4) regulates the feeling function: the experience and expression of emotions.
It allows you to feel your feelings and connect to others through empathy, but overuse (or misuse) can lead to oversensitivity, insensitivity, or emotional manipulation.
The Head / Thinking Center
The “head” or “intellectual” center (Points 5, 6, and 7) regulates the thinking function, which is the experience and expression of thoughts, beliefs, and other cognitive activities.
While essential for dispassionate analysis and reasoning, this form of intelligence can paralyze you if you overanalyze a situation.
Enneagram Wings
Everyone is a mixture of their primary type, and usually, one of the two adjacent to it on the circumference of the Enneagram.
The types adjacent to your primary type are your Wings.
Your primary type dominates your overall personality.
In contrast, the Wings complements it and adds essential, sometimes contradictory, elements to your character.
Your Wings are the “second side” of your personality and must be considered to better understand yourself or someone else.
Some individuals have both Wings, while others are strongly influenced by their primary type and show little of either Wing.
Here are the titles for the nine types with their Wings:
- 1 with Wing 9 – The Idealist
- 1 with Wing 2 – The Advocate
- 2 with Wing 1 – The Servant
- 2 with Wing 3 – The Host/The Hostess
- 3 with Wing 2 – The Charmer
- 3 with Wing 4 – The Professional
- 4 with Wing 3 – The Aristocrat
- 4 with Wing 5 – The Bohemian
- 5 with Wing 4 – The Iconoclast
- 5 with Wing 6 – The Problem Solver
- 6 with Wing 5 – The Defender
- 6 with Wing 7 – The Buddy
- 7 with Wing 6 – The Entertainer
- 7 with Wing 8 – The Realist
- 8 with Wing 7 – The Maverick
- 8 with Wing 9 – The Bear
- 9 with Wing 8 – The Referee
- 9 with Wing 1 – The Dreamer
Enneagram Subtypes
Subtypes exist within each of the nine types, broken down into three distinct versions according to how the passion (the primary type) combines with one of three instinctual biases (drives):
- Self-Preservation
- Social Interaction / Adaptive
- Sexual / Attraction / One-to-One Bonding
When passion and the dominant instinctual drive come together, they create a specific focus of attention, reflecting a particular insatiable need that drives behavior.
These subtypes thus reflect three different “subsets” of the patterns of the nine types that provide even more specificity in describing the individual’s personality.
All three instincts operate in all of us. Still, usually, only one is dominant in each individual. When the powerful biological drive of that dominant instinct is put in service of the “passion,” it fuels a more specific expression of the personality, resulting in a more nuanced character (a subtype) of the primary personality type.
Self-Preservation
- The Self-Preservation instinct focuses on and shapes behavior around survival and material security issues.
- It generally directs energy toward safety and security concerns, including having enough resources, avoiding danger, and maintaining a basic sense of structure and well-being.
- Beyond these fundamental concerns, the self-preservation instinct may emphasize other security areas regarding whatever that means for a person of a specific type (once it mixes with one of the nine passions).
- The Self-preservation instinct is related to the Root Chakra.
Social Interaction
- The Social instinct focuses on and shapes behavior around belonging, recognition, and relationships in social groups.
- It drives us to “get along with the herd”—our family, the community, and the groups we belong to.
- This instinct also relates to how much power or standing one has relative to the other members of “the group” regarding whatever that might mean for a person of a specific type.
- The Social instinct is related to the Solar Plexus Chakra.
Sexual / One-to-One Bonding
- Sexual instinct focuses on and shapes behavior around issues related to the quality and status of relationships with specific individuals.
- It generally directs energy toward achieving and maintaining one-to-one connections, interpersonal attraction, and bonding.
- This instinct seeks a sense of well-being through one-to-one connections with people, whatever that means for a specific type of person.
- Sexual instinct is related to the Sacral Chakra.
Enneagram Countertypes
There is a “countertype” subtype for each of the nine types.
In every case, with each of the nine points of the Enneagram, two subtypes go with the flow of the energy of the passion, and there is an upside-down one: one that doesn’t look like the others and goes against the main energetic direction of the desire.
This “counter-passional” type is the “countertype” of the three subtypes.
For example, the “counter-phobic” Sexual Six is the most well-known of the countertypes. It’s a Six who’s unafraid.
The passion of the Six is Fear, but the Sexual subtype goes against fear by being intense and intimidating to cope with anxiety.
The Nine Enneagram Types
Enneagram Type 1 – The Reformer
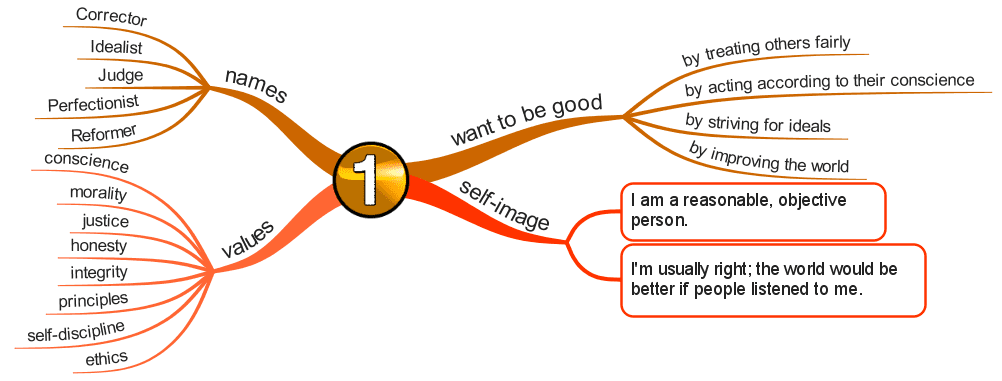
The Rational, Idealistic Type
- Principled
- Purposeful
- Self-Controlled
- Perfectionistic
Fear of being evil or corrupt
- They strive to be morally upstanding and virtuous in the face of external corruption.
- Their pervasive, underlying fear is that they are corrupt, and they must act virtuously to prove this fear wrong.
- Their prime motivation in life is their sense of integrity.
- They constantly aim to move away from corruption and towards virtue or the greater good.
Basic Desire
- To be good.
- To have integrity.
- To be balanced.
Key Motivation
- You are motivated by the need to live correctly, including improving yourself and the world around you.
- You strive to be consistent with your ideals and to justify yourself.
- To be beyond criticism so as not to be condemned by anyone.
Key Wounds
- You feel that something is wrong with you.
- You feel imperfect and need to do things well.
- You develop an inner critic.
- You think you have to do things the right way and adhere to specific standards of behavior.
Center of Intelligence
The Gut / Body / Instinctive – Anger / Rage
- Internalizes or focuses their anger inwardly.
- This leads to a perfectionistic streak.
- Since they give themselves no mercy, they also tend to be judgmental of others.
- They are principled, purposeful, self-controlled, and perfectionistic.
Learn more about the Enneagram Type 1 Personality.
Enneagram Type 2 – The Helper
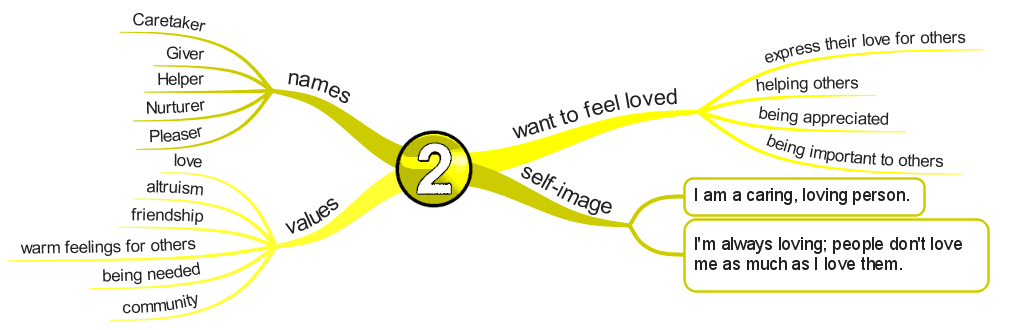
The Caring, Interpersonal Type
- Demonstrative
- Generous
- People-Pleasing
- Possessive
Fear of being unloved or unwanted by others
- They strive to be loved and wanted by those around them.
- Their pervasive, underlying fear is that there is nothing inherently loveable about them, and they must help others earn their love.
- Their prime motivation is proving themselves worthy of care and love from others.
- They constantly aim to move away from worthlessness and toward relationships that foster mutual loving and caregiving.
Basic Desire
- To feel loved.
Key Motivation
- To be worthy of care and love from others.
Core Wounds
- Your needs for love and attention go unmet.
- You develop a belief that your needs are less important than others.
- You manipulate the outer world to get your inner needs met.
- You believe it is selfish to have your own needs met.
- You take care of others to earn their love.
Center of Intelligence
The Heart / Feeling – Shame
- Externalizes or focuses their shame outwardly.
- Their shame is your problem and, thus, your problem to solve.
- If you give them enough feedback that they’re of value to you, it soothes their soul.
- They’ll do whatever they can to get that feedback and are often focused on meeting others’ needs while neglecting their own.
- They are generous, demonstrative, people-pleasing, and possessive.
Learn more about the Enneagram Type 2 Personality.
Enneagram Type 3 – The Achiever
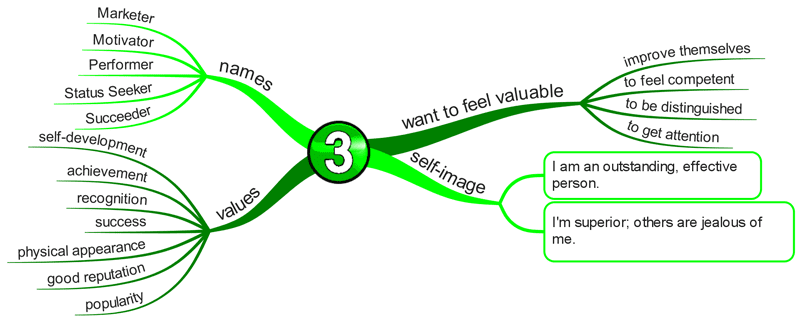
The Success-Oriented, Pragmatic Type
- Adaptive
- Excelling
- Driven
- Image-Conscious
Fear of being unaccomplished and worthless
- They strive to achieve success within their community, believing it to be a measure of their worth.
- This type’s pervasive, underlying fear is that they are inherently worthless and undesirable apart from their achievements.
- Therefore, they must accomplish as much as possible to be desired and accepted by others.
- They are constantly aiming to move away from worthlessness and towards impressive achievements that will earn them the respect and admiration of others.
Basic Desire
- To feel valuable and worthwhile.
Key Motivation
- The respect and admiration of others.
Core Wounds
- You feel inadequate, incompetent, a failure, incapable of caring for yourself.
- You believe you have to be the best to be valued or loved.
- You feel loved only for your accomplishments and not for who you are.
- You are focused on success.
Center of Intelligence
The Heart / Feeling – Shame
- Represses shame as a primary strategy.
- Like 9, they have a distaste for intrinsic anger.
- They are forever escaping their secret fear of having no value or worth.
- They are driven, adaptable, excelling, and image-conscious.
Learn more about the Enneagram Type 3 Personality.
Enneagram Type 4 – The Individualist
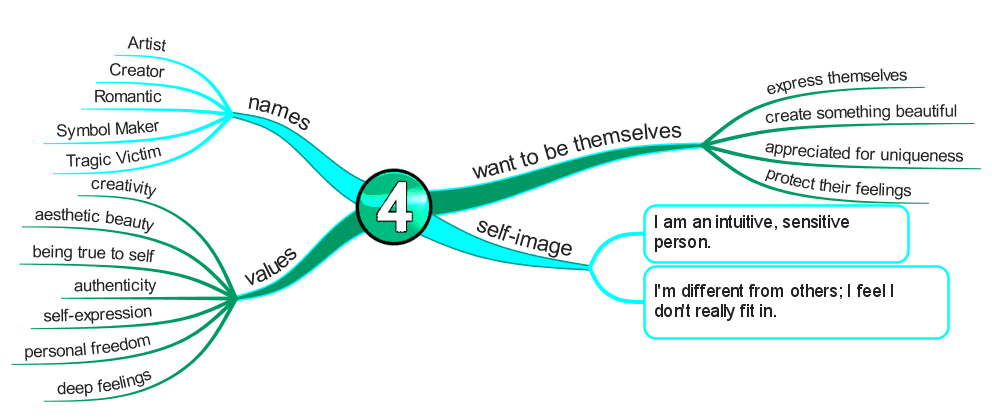
The Sensitive, Withdrawn Type
- Expressive
- Dramatic
- Self-Absorbed
- Temperamental
Fear of lacking a unique, significant identity
- They strive to prove their uniqueness and individuality to others.
- Their pervasive, underlying fear is that they would be worthless and unlovable if they were average.
- Therefore, they must cultivate as unique an identity as possible to prove their significance.
- They constantly aim to move away from normalcy and towards expressions of intensity and individuality.
Basic Desire
- To find themselves and their significance (to create an identity).
Key Motivation
- To be and express themselves.
Core Wounds
- You feel estranged, alienated, misunderstood, or different.
- Your search for an ideal self that will be seen as loveable and acceptable.
Center of Intelligence
The Heart / Feeling – Shame
- Internalizes, or focuses their shame, inwardly.
- There’s no way anyone else could understand what they deal with, and they are wholly unique.
- The desire for uniqueness and emotional depth gives a feeling of artistic melancholy on average Fours.
- They tend to be intuitive, unique, self-absorbed, and temperamental.
Learn more about the Enneagram Type 4 Personality.
Enneagram Type 5 – The Investigator
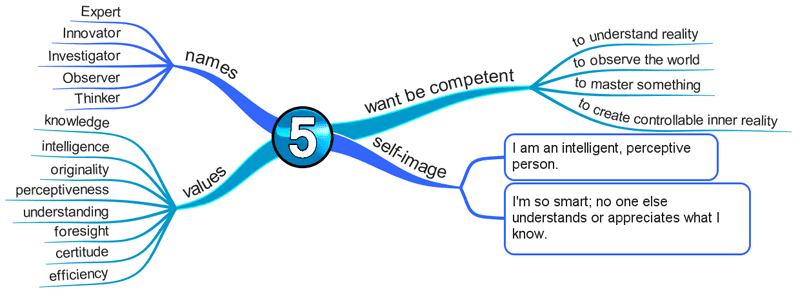
The Intense, Cerebral Type
- Perceptive
- Innovative
- Secretive
- Isolated
Fear of being helpless and inadequate
- They strive to become as knowledgeable and competent as possible in their undertakings.
- Their pervasive, underlying fear is being helpless, overwhelmed, and incapable of dealing with the world around them.
- Therefore, they must learn and master as much as possible to reassure themselves that they are competent.
- They constantly aim to move away from ignorance and ambiguity and toward knowledge and understanding.
Basic Desire
- To be capable.
Key Motivation
- To be competent.
Core Wounds
- You feel small, isolated, empty, alone, abandoned, and without support.
- You believe that knowledge will give you recognition and safety.
- You feel detached and compartmentalized.
Center of Intelligence
The Head / Thinking – Fear
- Externalizes or experiences their fear outwardly.
- The world is a scary place.
- Preparation is the key to dealing with it.
- They are forever in strategy mode, knowing if they can hone their skills enough, they’ll be ready for the scary world ‘out there.’
- They tend to be perceptive, innovative, secretive, and isolated.
Learn more about the Enneagram Type 5 Personality.
Enneagram Type 6 – The Loyalist
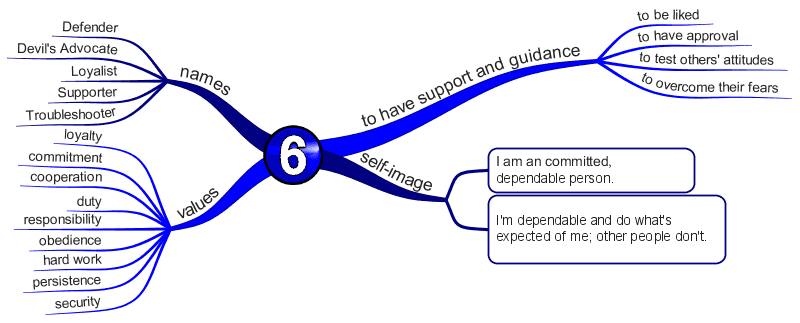
The Committed, Security-Oriented Type
- Engaging
- Responsible
- Anxious
- Suspicious
Fear of being without support or guidance
- They strive to find support and guidance from those around them.
- Their pervasive, underlying fear is that they cannot survive independently, and they must seek as much support and direction from others as possible.
- They are constantly aiming to move away from isolation and towards structure, security, and the guidance of others.
TBasic Desire
- To have security.
Key Motivation
- To feel supported.
Core Wounds
- You feel scared and insecure.
- You feel the world is unpredictable and untrustworthy.
- You believe the world is threatening and dangerous.
- You became defensively suspicious.
- You focus on being safe and secure.
Center of Intelligence
The Head / Thinking – Fear
- Represses fear as a primary strategy.
- Like the 9s and 3s, 6s are just as good at pretending there is no reason to feel fear.
- They repress it by surrounding themselves with safety/security systems (often in the form of people) and being suspicious of the unfamiliar.
- Since they can neither trust themselves nor the outside world, they can’t experience it as fear. ‘ Sixes has a Janus-like quality.
- They are engaging, responsible, anxious, and suspicious.
Learn more about the Enneagram Type 6 Personality.
Enneagram Type 7 – The Enthusiast
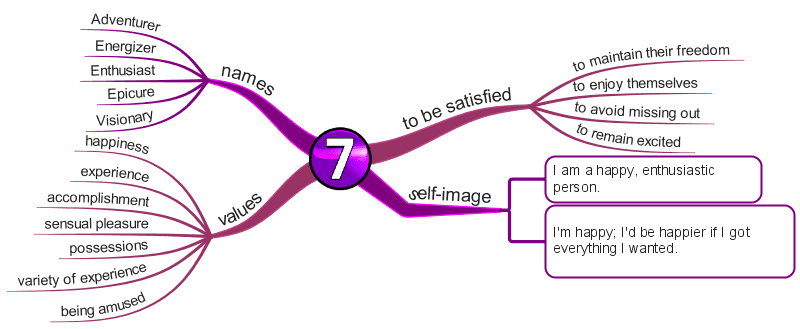
The Busy, Fun-Loving Type
- Spontaneous
- Versatile
- Distractible
- Scattered
Fear of deprivation and pain
- They strive to achieve their wildest desires and find fulfillment.
- Their pervasive, underlying fear is that others will not meet their needs and desires, so they must pursue them themselves.
- They constantly aim to move away from pain, sadness, and helplessness and towards independence, happiness, and fulfillment.
Basic Desire
- To be satisfied and content—to have their needs fulfilled.
Key Motivation
- To be happy and satisfied through many experiences.
Core Wounds
- You feel deprived and frustrated.
- You feel limited nurturing.
- You feel an inner emptiness.
- You fear that there will not be enough.
- You believe the source of satisfaction is outside yourself and need to find it yourself.
Center of Intelligence
The Head / Thinking – Fear
- Internalizes, or experiences, their fear inwardly.
- The outside world is fun, but there are dragons inside.
- They flee from the inner world and gorge on the outer world of pleasures and possibilities.
- They tend to be versatile, acquisitive, spontaneous, and scattered—a total blast to be around—but tough to pin down.
Learn more about the Enneagram Type 7 Personality.
Enneagram Type 8 – The Challenger
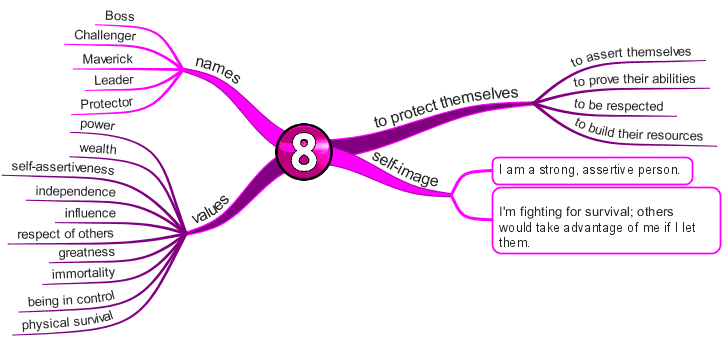
The Powerful, Dominating Type
- Self-Confident
- Decisive
- Willful
- Confrontational
Fear of being harmed or controlled by others
- They strive to become firm, independent, and self-directed.
- Their pervasive, underlying fear is being violated, betrayed, or arrested while at the mercy of others.
- They feel secure and okay as long as they maintain their circumstances.
- They constantly aim to move away from external limitations and toward self-sufficiency and power.
Basic Desire
- To protect themselves (to manage their own life and destiny).
Key Motivation
- To be self-reliant and stay in control.
Core Wounds
- You perceived the world as hostile.
- You believe you must be strong and not show vulnerability.
- You must protect yourself from being controlled or dominated.
- You project power and strength to cover up feelings of vulnerability.
- You believe you need to fight for survival.
Center of Intelligence
The Gut / Body / Instinctive – Anger / Rage
- Externalizes, or expresses, anger as the primary strategy for getting what they want and dealing with stresses/challenges.
- They tend to bulldoze through life and let you feel their anger if they don’t get it.
- They tend to be self-confident, decisive, willful, and aggressive.
Learn more about the Enneagram Type 8 Personality.
Enneagram Type 9 – The Peacemaker
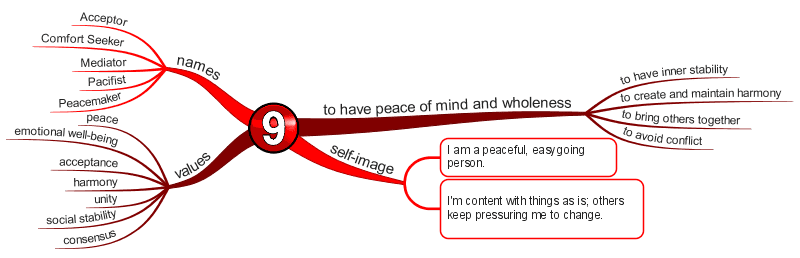
The Easygoing, Self-Effacing Type
- Receptive
- Reassuring
- Agreeable
- Complacent
Fear of loss and separation from others
- They strive to maintain peace and harmony internally and externally.
- Their pervasive, underlying fear is that they will become disconnected from others and out of sync with the world around them.
- They feel secure and okay as long as they live in harmony with the people and world around them.
- They constantly move from conflict and pain toward peace, stability, and harmony.
Basic Desire
- To have inner stability, “peace of mind.”
Key Motivation
- To have peace of mind and create harmony in their environment.
Core Wounds
- You feel the loss of connection to caregivers, to fear losing connection to others.
- Self-perception that you are unimportant, inadequate, and insignificant.
- You believe you need to forget yourself and accommodate others.
- You avoid strong opinions or drawing attention to yourself.
Center of Intelligence
The Gut / Body / Instinctive – Anger / Rage
- Represses anger as the primary strategy.
- They don’t like donating or acknowledging anger, so they tend to ‘smolder’ ‘underneath.
- They tend to be receptive, reassuring, and complacent.