
What is the DISC “Influencer” Behavioral Personality Style?
People with the Influencer DISC Behavior Style are Fast-paced and People-oriented.
They are enthusiastic, optimistic, talkative, persuasive, impulsive, and emotional.
Influential people emphasize bringing others into an alliance to accomplish results and prefer to focus on relationships over tasks.
They will trust others naturally, truly enjoy being around others, and function best when around people and working in teams.
Influencers are not afraid to be the center of attention.
Influencer Personality Type cross-reference
- Keirsey Type – Idealists
- Temperament Type – Phlegmatic
- Animal Type – Otter
- Socio-Communicative Type – Expressive
- True Colors – Blue
- Color Code – Blue
- Personality Compass – West
- Occupational Type – Artistic
- Learning Type – Theorist
- Leadership Type – Collaborator
MBTI Personality Types (xNFx) – Intuition and Feeling
Enneagram Types
- Type 1 – The Reformer (ENFJ, INFJ)
- Type 4 – The Individualist (INFJ, INFP)
- Type 7 – The Enthusiast (ENFP)
- Type 9 – The Peacemaker (INFP)
What is the DISC Behavioral Model?
The DISC Behavioral Model describes an individual’s characteristics, communication preferences, and motivation as observable behaviors.
Recognizing observable behaviors in others can help you communicate more effectively and build stronger relationships, personally and professionally.
Dr. William Marston theorized that people are motivated by two key motivators that direct human behavioral patterns: the Motor Drive (or Pace Driver) and the Compass Drive (or Priority Driver).
The Motor/Pace Driver
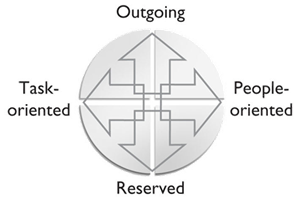
If you divide a circle in half horizontally, the upper half represents outgoing or fast-paced people. The lower half represents reserved or slower-paced people.
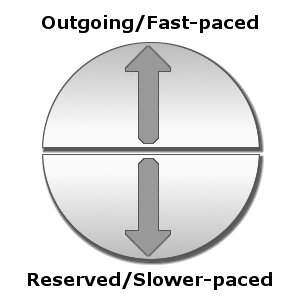
Outgoing people tend to move fast, talk fast, and decide quickly.
Reserved people tend to speak more slowly and softly and generally prefer to consider things carefully and thoroughly before deciding.
Remember that these descriptions of behaviors are tendencies rather than absolutes. Depending on the situation, most people will exhibit a bit of both of these Traits.
Even so, most people will exhibit more of one Trait over the other – even if it is slightly more.
The Compass/Priority Driver
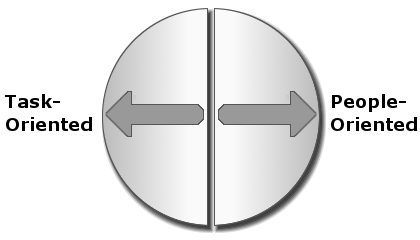
Now, divide the circle vertically, where the left half represents task-oriented people. The right half represents people-oriented individuals.
Task-oriented people focus on logic, data, results, and projects.
People-oriented individuals focus on experiences, feelings, relationships, and interactions with others.
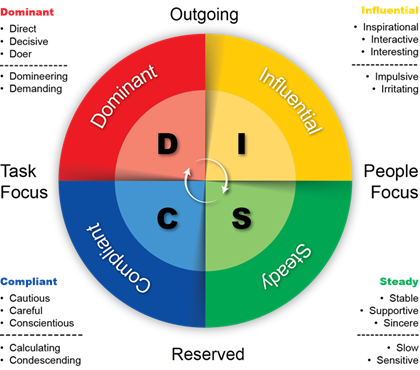
The Four DISC Behavioral Styles
When you combine the drawings for the Motor and Compass drives, you get the circle of expected behaviors and perspectives divided into four quadrants.

The DISC circle represents the full graphical description of what is commonly referred to as The DISC Model of Human Behavior.
Each quadrant of the DISC circle has descriptive words attached to it.
These descriptive words attempt to capture the typical behavior traits or tendencies people exhibit with the combination of motor and compass drives corresponding to that quadrant.
They are often called a behavioral type or style to make discussing the quadrants easier.
While it is not strictly or technically accurate from a clinical psychology standpoint to use the phrase personality type with this model, it is often used in everyday conversation.
So, the term Behavioral Style is preferred because it more accurately fits the model and its theory.
Learn more about the DISC Behavioral Personality Styles.
Personality Temperaments, Traits, and Types
Personality Temperaments, Personality Traits, and Personality Types are used in Psychology to discuss a person’s Personality, a collection of Emotions, Perceptions, and Actions that interact with each other, regulate themselves, and shape a dynamic system that forms a person’s Behavioral Patterns.
Your inherited Traits (your Personality Temperament), along with your acquired Traits (such as education, socialization, and other various pressures and aspects in your life), form your Personality.
A Personality Type identifies a specific collection of Traits, both learned and natural, that comprise a broad, general Personality Classification—a way of labeling a collection of traits and behaviors.
A Personality Trait remains consistent and stable over time, which means you exhibit the same pattern across different situations and throughout your life.
Three criteria characterize Personality Traits: (1) consistency, (2) stability, and (3) individual differences. For example, if you are talkative at home, you also tend to be talkative at work. And if you were talkative at age 20, you would still be chatty at age 40.
Personality Temperament is your “Naturally Intuitive” biological Trait. These Traits are partly inherited from your genes and partially determined by your brainstem, which doesn’t change throughout your life. These are Natural Traits regarded as innate or inborn and not learned.
Your Personality Temperament is formed as an infant and is hard to modify, manipulate, or change because it is genetic. In some way or another, your inherited behavioral tendency will always be there.
Personality Traits are the quantitative differences between people, and Personality Types are qualitative differences between people. The most crucial difference between the Trait Theory and Type Theory is that Type Theory views people’s characteristics as discrete categories. In contrast, Trait Theory views these characteristics as a continuum.
For example, where a Type Theorist would claim that introverts and extraverts are two types of people, a Trait Theorist claims extraversion is a gradient and individuals can fall somewhere in the middle.
Your Temperaments, along with acquired Traits, form your Personality.
Traits
- Sociable
- Talkative
- Enthusiastic
- Optimistic
- Spontaneous
- Agreeable
- Persuasive
Motivation
- Recognition
- Approval
- Popularity
- Acceptance.
Annoyances
- Disinterest
- Slowness
- Pessimism
- Details
- Time restraints
- Structure
- Lack of enthusiasm
Under pressure
- Hyper
- Overly optimistic
- Emotional
Weaknesses
Influence people are not good with details and are more concerned with people and popularity than with tangible results and organization.
It’s also possible they are not great listeners and may give the impression of waiting to speak instead of genuinely listening to what someone else is saying.
In some cases, gestures and facial expressions are overly used.
Because they have so many ideas and enjoy discussing them, it may take some planning to turn their verbal ideas into action.
It helps them have someone write details down for them or check back occasionally to ensure action items are being done to expectation and on point.
Rejection is their biggest fear since others’ acceptance and approval is their primary desire.
Team Value
Influence people are naturally creative problem solvers who can think outside the box.
They are great at encouraging and motivating others to take action.
Influence people keep a positive environment with enthusiasm, optimism, and a cheerful sense of humor.
They will go out of their way to keep things light, avoid and negotiate conflict, and keep the peace.
- They are intuitive communicators and create an atmosphere of well-being.
- They are spontaneous and agreeable and respond well to the unexpected.
- They express their ideas well and make good spokespersons.
- They accomplish goals through people and work well with others.
- They will offer their opinions and can be persuasive.
- They are enthusiastic, have a positive attitude, and have a good sense of humor.
- They are also perfect for brainstorming sessions.
Ideal Environment
Influence people require a place that does not feel rigid and controlled.
They are happiest with few conflicts and arguments, with other people around, and with some flexibility. However, they do not like focusing on details or spending much time alone.
Give them plenty of opportunities to verbalize their ideas, as they usually have creative thoughts and are great problem solvers.
They need a forum to express ideas and love group activities in professional and social environments.
Influence people enjoy freedom from too many rules or regulations and gravitate towards a friendly and fun environment.
They thrive when they can be the talker, the presenter, the main person who builds rapport, or have a strong influence when working in teams but need another person to handle the details.
Allow time for social activities at work; they are great motivators of others.
Leadership Style
They tend to take a “democratic” approach and facilitate communication and initiative by others.
- People with much energy and enthusiasm constantly rise to the top in leading others.
- They love to impress and inspire others to follow.
- They are not confrontational.
- They use their tremendous people skills to create exciting climates for growth.
- They love to be upfront and have excellent verbal skills.
- They struggle between what people think of them and moving forward.
- They often come across as proud or egotistical but are best at leading groups through their optimistic attitudes.
Follower Traits
- Follow with their heart.
- They tend to be impulsive followers.
- They want opportunities that will make them look good.
- Talk a lot; they make good first impressions.
- High egos and the ability to persuade often turn them into leaders to rise to the top.
- Sometimes, you don’t know who is leading whom.
Communication Styles
- Try to be a good listener.
- Try not to exaggerate too much.
- Try to focus on details and facts.
Influencer People
- Try to be a good listener and show enthusiasm.
- Try to emphasize the good and positive when making your point.
Dominate People
- Be serious rather than silly or informal.
- Don’t waste time.
Steady People
- Be sensitive and stay calm.
- Don’t interrupt.
Compliant People
- Be factual, precise, and methodical, and give details.
- Ask exploratory questions.
Teaching Style
- They tell the best stories and use clear illustrations.
- Their verbal skills create fascinating studies, but they tend to have lengthy classes.
- They need to be more time conscientious.
- They may also stretch the text to make a point.
- Concerned about what others think, they often make good impressions.
- They can become prideful because of their tremendous communication ability.
- They are some of the most exciting instructors.
Learning Styles
Kinesthetic Learner
- Wants to FEEL part of the lesson.
- Desires an emotional tie with the presenter and the task’s point.
- Learns best in a group where their feelings can be expressed.
- Needs heartfelt communication.
Visual Learner
- Wants to SEE the lesson through drama or role-play.
- Desires to participate by acting out or visualizing the task.
- Learns best when able to picture themself in the job.
- Look for images that explain the job.
Auditory Learner
- LISTENS best to exciting and enthusiastic communication.
- Desires to hear expressions and word pictures that make lessons come alive.
- Needs to hear influencing and impressive learning that communicates optimism.
- Hears the study best through humorous stories.



