What is the Keirsey INTJ “Mastermind” Personality Type?
The Keirsey INTJ “Mastermind” Personality Type is a Rational Temperament with an Abstract Communication Style and a Utilitarian Action Style.
Keirsey organized the Four Temperaments as a matrix. There are two communication styles, abstract and Concrete, similar to the Myers-Briggs Intuition (Abstract) and Sensing (Concrete) “Perceiving” Cognitive Functions.
And by two action styles: cooperative and utilitarian. Utilitarian people, for the most part, do what works, while Cooperative people do what’s right.
Keirsey named the Four Temperaments as suggested by Plato: Artisan (Iconic), Guardian (Pistic), Idealist (Noetic), and Rational (Dianoetic).
Concrete versus Abstract Communication Style
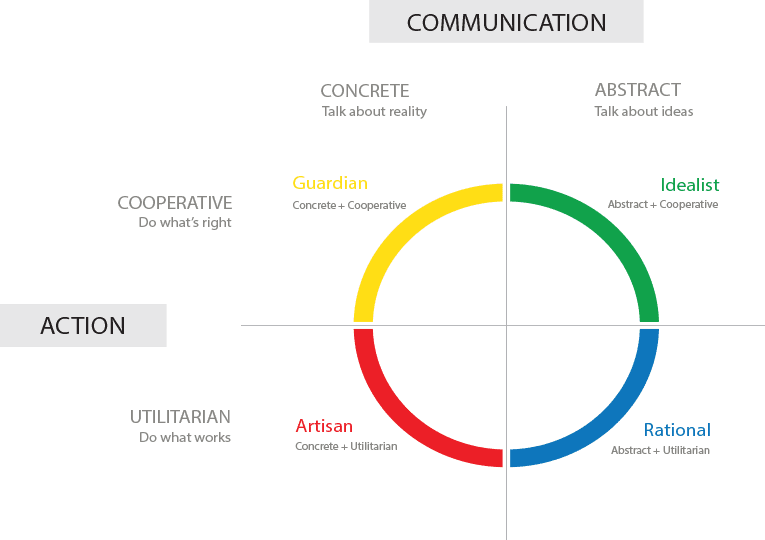
Keirsey divided the Four Temperaments into two Communication Styles: Abstract and Concrete. These styles resemble the Myers-Briggs Intuition and Sensing “Perceiving” Cognitive Functions.
Some people talk primarily about everyday reality’s external, concrete world: facts and figures, work and play, home and family, news, sports, and weather—all the who, what, when, where, and how of life.
Other people talk primarily about the internal, abstract world of ideas: theories and conjectures, dreams and philosophies, beliefs and fantasies—all the whys, ifs, and what might be of life.
Concrete people talk about reality in their daily lives, while Abstract people talk about ideas.
According to Keirsey, everyone can engage in both observation and introspection. People are observant when they touch objects or otherwise perceive the world through their five senses. When people reflect and focus on their internal world, they are introspective. However, individuals cannot engage in observation and introspection at the same time. The extent to which people are more observant or reflective affects their behavior.
People who are generally observant are more ‘down to earth.’
They are more concrete in their worldview and focus on practical matters such as food, shelter, and immediate relationships. Carl Jung used the word sensation to describe people who prefer concrete perception.
Generally, reflective people have more ‘heads in the clouds’ and abstract worldviews. They focus on global or theoretical issues such as equality or engineering. Carl Jung used the word intuition to describe people who prefer abstract perception.
Cooperative versus Utilitarian Action Style
Some people act primarily practically or pragmatically; that is, they do what gets results, what achieves their objectives as effectively or efficiently as possible. They only check afterward to see if they observe the rules or go through the proper channels.
Other people act primarily cooperatively or socially acceptable; they try to do the right thing in keeping with agreed-upon social rules, conventions, and codes of conduct. Only later do they concern themselves with the effectiveness of their actions.
These two ways of acting can certainly overlap, but as they lead their lives, utilitarian people mostly do what works, while cooperative people do what’s right.
Keirsey compares the differing temperaments with cooperative (Complying) and pragmatic (Adaptive) temperaments. Cooperative people pay more attention to other people’s opinions and are more concerned with doing the right thing. Sensible people (Utilitarian) pay more attention to their thoughts or feelings and are more concerned with doing what works. No comparable idea in the MBTI or Jung corresponds to this dichotomy, which is a significant difference between Keirsey’s work and Myers and Jung’s.
The pragmatic temperaments are Rational (pragmatic and abstract) and artisan (Pragmatic and concrete). The Cooperative Temperaments are Idealists (Cooperative and Abstract) and Guardians (Cooperative and Concrete). Neither the MBTI nor Jung included the concept of Temperament in their work.
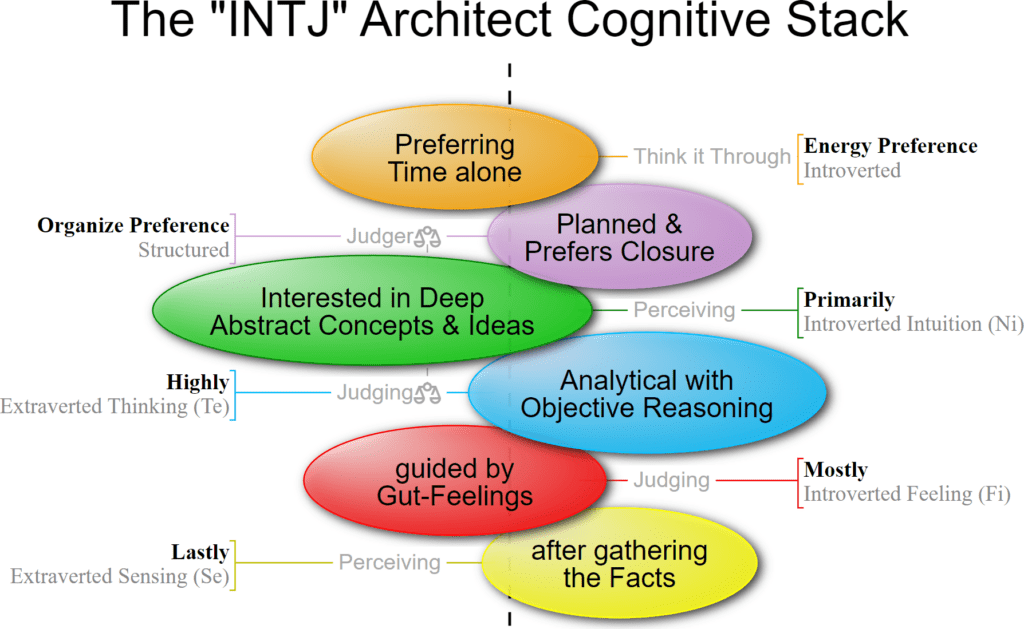
INTJ Keirsey/MBTI Correlation
| Keirsey | MBTI | |
|---|---|---|
| I | Attentive Role Variant | Introverted Intuition |
| N | Abstract Communication Style | Introverted iNtuition Dominate Function |
| T | Utilitarian Action Style | Auxiliary Extraverted Thinking Function |
| J | Directive Role | Thinking is a Judging Function |
With Introverted Intuition as the first Dominant Function and Extraverted Thinking as the second Auxiliary Function, the MBTI INTJ “Architect” Personality Type correlates to the Keirsey INTJ “Mastermind” Personality Type.
INTJ Personality Type cross-reference
- Keirsey Type – Mastermind
- Temperament Type – Choleric
- Animal Type – Lion
- DISC Type – Dominant
- Socio-Communicative Type – Driver
- True Colors – Green
- Color Code – Red
- Personality Compass – North
- Occupational Type – Enterprising
- Learning Type – Activist
- Leadership Type – Dominator
Enneagram Types
Mastermind Personality Characteristics
All Rationals are good at planning operations, but Masterminds are head and shoulders above all the rest in contingency planning.
Trying to anticipate every contingency, Masterminds never set off on a project without firmly in mind Plan Ad. They are always prepared to switch to Plan B, C, or D if need be.
Masterminds are rare, comprising no more than one percent of the population. And they are rarely encountered outside their office, factory, school, or laboratory.
Although they are competent leaders, Masterminds are not eager to take command. They prefer to stay in the background until others demonstrate their inability to lead. Once they take charge, however, they are thoroughgoing pragmatists.
Masterminds are convinced that efficiency is indispensable in a well-run organization. If they encounter inefficiency—any waste of human and material resources—they quickly realign operations and reassign personnel.
Masterminds do not feel bound by established rules and procedures. Traditional authority does not impress them, nor do slogans or catchwords.
Only ideas that make sense to them are adopted; those that don’t aren’t, no matter who thought of them. Remember, their aim is always maximum efficiency.
In their careers, Masterminds usually rise to positions of responsibility. They work long and hard and are dedicated to pursuing their goals. They spare neither their own time and effort nor that of their colleagues and employees.
Problem-solving is highly stimulating to Masterminds, who love responding to tangled systems requiring careful sorting.
Ordinarily, they verbalize the positive and avoid comments of a negative nature.
They are more interested in moving an organization forward than dwelling on past mistakes.
Masterminds tend to be much more definite and self-confident than other Rationals, having usually developed a strong will.
Decisions come quickly to them; they can hardly rest until things are settled and decided. But before they decide anything, they must do the research.
Masterminds are highly theoretical but insist on looking at all available data before embracing an idea.
They are suspicious of any statement based on shoddy research or not checked against reality.
Famous Masterminds
Alan Greenspan, Ben Bernanke, Dwight D. Eisenhower, General Ulysses S. Grant, Friedrich Nietsche, Niels Bohr, Peter the Great, Stephen Hawking, John Maynard Keynes, Lise Meitner, Ayn Rand and Sir Isaac Newton are examples of Rational Masterminds.

What are the Keirsy Personality Temerpaments?

David Keirsey, born in 1921, was an American psychologist specializing in conflict management and family counseling. He began researching human behavior and Personality in the 1940s.
Keirsey blended the Myers-Briggs Personality Types with Ernst Kretschmer’s model of the Four Temperaments, developing the Keirsey Temperament Sorter, which was made famous by his book “Please Understand Me.”
Instead of using the term Personality, Keirsey used Temperament. He viewed it as a configuration of observable Personality Traits, communication habits, patterns of action, characteristic attitudes, values, and talents. To Keirsy, Temperament encompasses personal needs, individual contributions, workplace contributions, and societal roles.
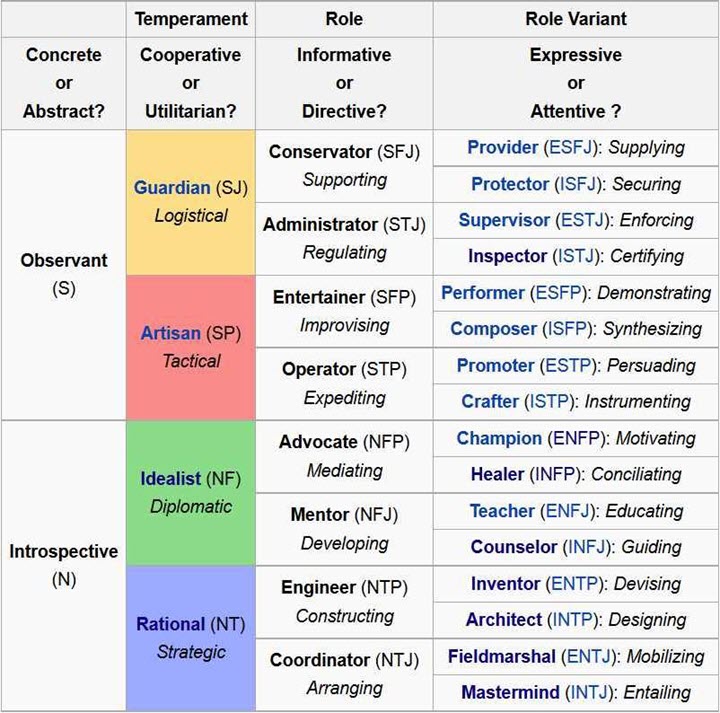
Keirsey correlated the sixteen MBTI Personality Types into Four Temperaments. He divided each Temperament into two Roles: informative and Directive. He subdivided the roles into expressive (extraverted) and attentive (introverted) role Variables.
Informative versus Directive Roles
Keirsey distinguishes between people who generally communicate by informing others versus those who speak by directing others. This distinction subdivides each of the four Temperaments into eight Roles.
Expressive versus Attentive Role Variants
Individuals who act before observing are Expressive. In contrast, people who follow before working are Attentive.
Expressive and attentive variants further subdivide the eight roles into 16 types correlating to the 16 Myers-Briggs personality types.