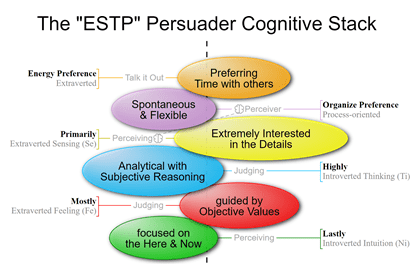
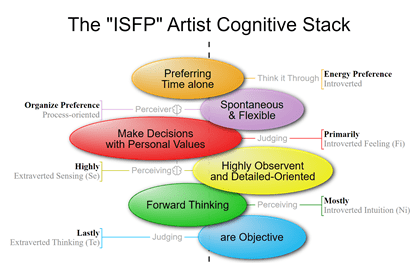
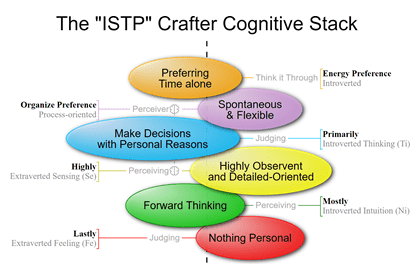
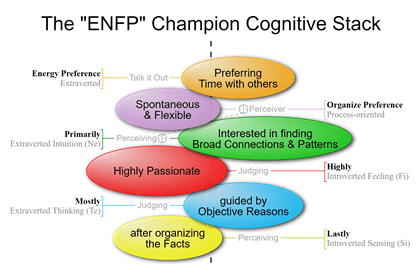
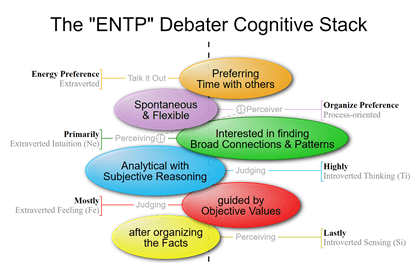
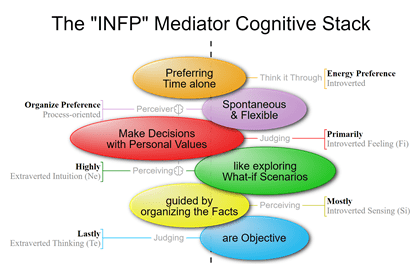
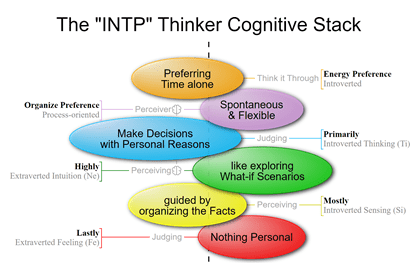
What is the MBTI – Myers-Briggs Type Indicator?

The MBTI is a personality test based on Carl Jung’s Psychological Types Theory. Carl Jung’s theory of psychological types suggested that people have four psychological functions: Judging, Perceiving, Introversion, and Extraversion.

Katharine Briggs and Isabel Briggs-Myers, a mother-daughter duo, initially created the Myers-Briggs Type Indicator (MBTI) in 1942. Their goal was to make Carl Jung’s theories more understandable and to assist women entering the workforce during World War II in finding suitable and adequate employment.
Although the MBTI Personality Typing System is extremely popular, it is often misunderstood and misused.
The MBTI is about how people prefer to learn and make decisions based on an individual’s Cognitive Preferences, not a person’s Cognitive Capabilities.
This is a crucial distinction, and it is often why so many people mistype themselves or think they want to be a different type.
There is no one Personality Type better than the others.
The other misunderstanding concerns the meaning or purpose of the four Cognitive Functions: Thinking, Feeling, Sensing, and Intuition, which are used when making decisions.
- Thinking is a judging function and your reason when making decisions.
- Feeling the other judging function focuses on your values when making decisions.
- Sensing is the function of perceiving the facts and details when making decisions.
- Intuition is the other perceiving function, and it involves thinking about how abstract concepts and ideas are used when making decisions.
The MBTI is about how we prefer to use these Cognitive Functions in a particular way when learning, making decisions, and communicating with others.
Each Cognitive Function has an internal (introverted) versus external (extraverted) orientation. Introverted Thinking and Feeling are your subjective reasons and values. On the other hand, extraverted Thinking and Feeling are your objective reasons and values.
Extraverted Sensing is about gathering the Facts, whereas Introverted Sensing is about organizing the Facts. Introverted Intuition is about thinking deeply about something, while Extraverted Intuition is about thinking broadly and connecting the dots across things.
From this explanation, you may recognize your preference for using these functions when making decisions. Do you base your decision on your reasons, values, facts, or more abstract concepts and ideas?
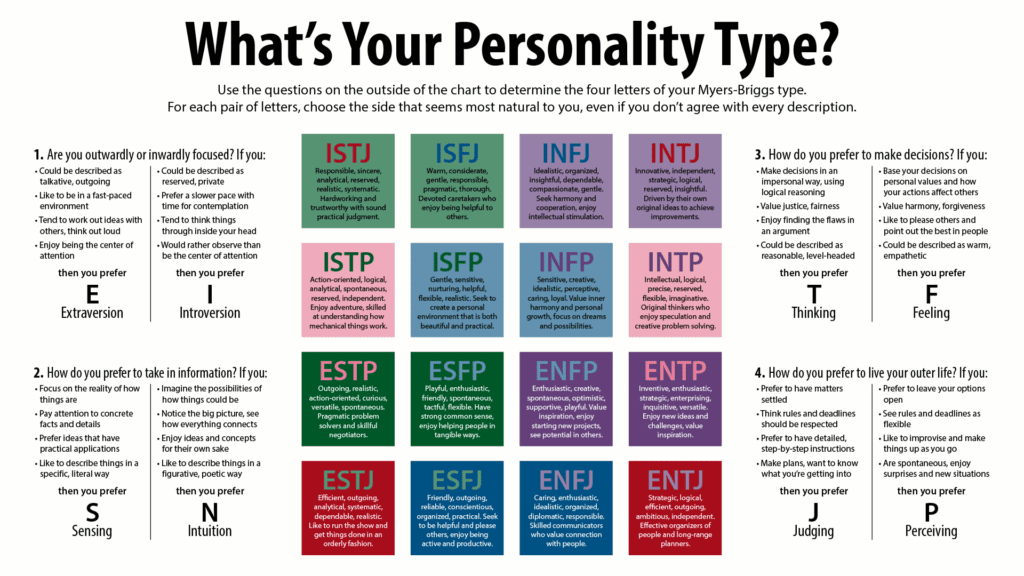
Of course, people don’t fit perfectly into only 16 types, but the MBTI is a tool to help you better understand how you prefer to learn and make decisions using four Cognitive Functions.
You must be honest with yourself to get real value from the MBTI. The MBTI is not a competition. It’s intended to help you understand yourself and others better by explaining how people prefer to communicate.
The official MBTI® assessment is owned and licensed by The Myers-Briggs Company. However, our simple three-question quiz can help you quickly identify your type.
- First, are you organized or prefer to be more flexible?
- Second, are you more Results-oriented, Process-oriented, Detailed-oriented, or Idea-oriented?
- And last, do you prefer your Reasons or Values when making decisions?
Extraversion versus Introversion
Often, people refer to Extraversion and Introversion as their energy source, meaning they are externally energized or motivated by the world outside themself or internally energized or motivated from within themselves.
The Extraversion Trait, as defined by the Big Five Personality Traits model, measures Extraversion on a scale where High Extraversion is what you expect; a person is outgoing and People-Oriented. In comparison, a person who scores Low in Extraversions is an Introvert.
However, Extraversion and Introversion within the MBTI context have little to do with outgoingness, sociability, or social confidence. They are not Personality traits but orientations for each Cognitive function.

It’s helpful to interpret Introverted to mean Subjective and Extraverted to mean Objective within Thinking and Feeling-Judging Cognitive Functions.
For instance, consider Introverted Thinking as your Subjective/Personal Reasons and Introverted Feeling as your Subjective Values. Conversely, interpret Extraverted Thinking as your Objective Reasons and Extraverted Feeling as your Objective Values.
Within the Sensing Perceiving Cognitive Function context, it helps to interpret Introverted as Organizing and Extraverted as Gathering. For instance, Introverted Sensing organizes the Facts and Details, whereas Extraverted Sensing gathers them.
Within intuition-perceiving cognitive function, interpreting intrinsic Intuition as abstract concepts and ideas is more beneficial than interpreting extraverted Intuition as more creative and proven ideas.
Sensing and Intuition Perceiving Functions
Consider the situations below and reflect on whether you prefer Sensing or Intuition when considering your cognitive preference.
What kind of instructions works well for you?
Do you prefer step-by-step, practical instructions that are clear and accurate (S), or do you like to be given the overall purpose and work it out for yourself (N)?
Imagine you assembling something…
Do you follow the instructions (S) or give it a go (N)?
How do you approach learning something new?
Do you like to try things out and experience, focusing on learning with a practical application (S), or instead, explore how learning fits other ideas and imaginatively (N)?
What information do you need when buying something?
The facts, specifications, and details to see if it will meet your needs (S) or an overview and imagine how the product will work for you, a vision of the future, and how you will use it (N)?
The Sensing (S) Function
Sensing refers to processing data through the five senses.
Characteristics:
- You want to know the facts.
- You look at specifics.
- You collect observations about the world.
Extraverted Sensing (Se)
Extraverted Sensing is about gathering data and a strong awareness of the physical world.
You experience the sights, sounds, and smells of the world around you to your fullest extent and act on your experiences immediately.
Characteristics:
- You experience and notice all the concrete details in the outer world.
- You are highly attuned to environmental changes and scans for visible reactions and relevant data.
- You adapt and change with the existing environment and tune into the moment to maximize the experience and respond.
- You focus on the facts and are highly realistic.
Introverted Sensing (Si)
Introverted Sensing is storing and organizing the data and then comparing that data with previous experiences.
For example, when you see a movie that reminds you of another similar movie or when you see someone who reminds you of someone else.
You also use past experiences to learn how to handle similar current situations.
Characteristics:
- You review your experiences to compare and contrast what has been.
- You clarify and accumulate detailed information and systematically complete projects.
- You preserve vivid impressions, remembering exactly how something once was and its appearance.
- You notice changing patterns and are attentive to alterations and modifications.
- You are very practical and detail-oriented.
The Intuition (N) Function
Intuition refers to how people process data, looking for meaning and patterns behind the information.
Characteristics:
- You seek out new ideas.
- You ensure things work in theory.
- You use conceptual frameworks.
Extraverted Intuition (Ne)
Extraverted Intuition involves seeing all possibilities of a subject. People who prefer Extraverted Intuition can juggle many ideas simultaneously and enjoy brainstorming.
Characteristics:
- You see numerous theoretical possibilities, connections, and relationships between things in the outside world.
- You read between the lines and explore potential possibilities.
- You have an ever-shifting pattern of ideas and insights triggered by recent experiences.
- You see everything in the context of how it relates to everything else. Nothing stands alone or is disconnected.
Introverted Intuition (Ni)
People who prefer Introverted Intuition think about the future by processing signs, trends, and patterns through impressions and meanings. They find relationships between similar ideas to look for a central concept.
Characteristics:
- You foresee implications, conceptualize new ways of seeing things, and get an image or sense of the future or profound hidden meaning.
- You feel confident about what will happen and are energized by transformational visions of how something will develop.
- You receive “flashes” of insight and are tapped into universal symbols.
Thinking and Feeling Judging Functions

Just because someone has a Thinking preference doesn’t mean they don’t have Feelings! And just because someone has a Feeling preference doesn’t mean they don’t Think about things!
Thinking and Feeling are judging functions used when making decisions, while Sensing and Intuition are perception functions. Generally, those who prefer to gather information are Perceiving, while those who like making decisions are Judging.
The Thinking (T) Function
Thinking refers to how people make decisions based on reasons. Introverted Thinking people base their decisions on personal grounds. On the other hand, extroverted thinking people base their decisions on considering objective reasons.
Characteristics:
- You apply logical reasoning.
- You use cause-and-effect analysis.
- You focus on the tasks.
Extraverted Thinking (Te)
Extraverted Thinking helps to create order out of chaos and organizes the environment through charts, graphs, outlines, etc.
Extraverted Thinking allows you to determine what is necessary and determine the most efficient way to complete an objective.
People who prefer Extraverted Thinking love a challenge because it tests your skills, and you almost always follow through on a project.
Characteristics:
- You apply logic, order, and efficiency to the outer world.
- You quickly notice inefficiency or flaws in a system or plan and are skilled at streamlining processes.
- You express thoughts directly and are skilled at critiquing, directing, and organizing.
- You take decisive action and focus on objective logic and data to make decisions and create plans.
- You appreciate empirical evidence and dislike paradoxes.
Introverted Thinking (Ti)
Introverted Thinkers find ways to express an idea that is to the point and concise.
People who prefer Introverted Thinking analyze, categorize, and evaluate to determine whether something fits into the larger framework. They often check for inconsistencies and disassemble things to understand how they work. You use models to see how things should be and look at both sides of issues to determine inconsistencies.
Characteristics:
- You notice the fine distinctions between things and create categories and sub-categories to classify everything accurately and precisely.
- You examine many sides of an issue, always seeking the truth and looking for accuracy.
- You like to learn for the sake of learning.
The Feeling (F) Function
The Feeling Function guides how people make decisions based on values. Introverted Feeling people base decisions on principles and personal matters. At the same time, Extraverted Feeling people are more objective and base their decisions on considering other people’s feelings and socially acceptable values.
Characteristics:
- You apply your values.
- You seek harmony.
- You focus on relationships.
Extraverted Feeling (Fe)
Extraverted Feelings involve considering other people’s feelings very seriously. People decide whether something is worth standing up for based on its truth and significance to objective values.
People who prefer Extraverted Feelings often try to help everyone get along. For example, you may disclose your feelings and take on others as your own.
They like determining what will work best for the group while honoring and considering everyone’s values and feelings. They will accommodate themselves and others by deciding what is appropriate and acceptable in that setting.
Characteristics:
- You connect and empathize with others while responding to their values and feelings.
- You monitor the environment for morale or disharmony and create an environment where people feel happy and welcome.
- You “Absorb” other people’s emotions in real time to sense their feelings.
Introverted Feeling (Fi)
Introverted Feelings involve deciding whether something is worth fighting for based on its validity and significance to your subjective values. People with Introverted Feelings often have feelings about a person’s essence, which helps them determine if something is fake or genuine. People with Introverted Feelings communicate through actions and emotions rather than words.
Characteristics:
- You consider what is essential and what one’s subjective values are.
- You notice inconsistencies between actions and espoused values and are very attuned to what is authentic or inauthentic.
- You are highly aware of what feels right or wrong to yourself and strive to live by that.
- You continually weigh the situational worth or importance of everything.
- Most of the time, you express your values through action rather than words.
Are you a Judger or Perceiver?

Judging does not mean you are “judgmental,” and Perceiving does not mean you are “perceptive.”
Thinking and Feeling are Judging functions, while Sensing and Intuition are Perceiving functions.
The topmost Extraverted Function, which may be the first function, the Dominant Function, or the second function, the Auxiliary Function; whichever is the top Extraverted Function, determines if you are a Judger or a Perceiver type of person.
If our highest Extraverted Function is decision-making, you prefer Judging. If your highest Extraverted Function is information-gathering, you prefer Perceiving.
For extraverts, your highest Extraverted Function is always the first function, the Dominant Function, whereas, for Introverts, your secondary function, the Auxiliary Function will always be the highest Extraverted Function.
So, if the last letter is a J, you have either the Thinking or Feeling as either your Dominant or Auxiliary function. If the last letter is a P, you have either the Sensing or Intuition function as your Dominant or Auxiliary function.
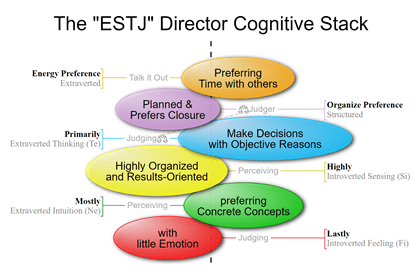
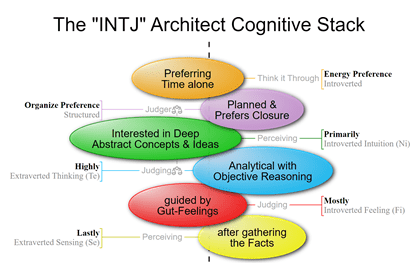
TJs prefer their Thinking function—rather than Feeling, Intuition, or Sensing functions—when dealing with the external world. In other words, TJs prefer to extravert their Thinking.
Similarly, FJs tend to extravert their Feelings. The TJs and FJs are the eight MBTI types that prefer to extravert their judging function.
J is a handy abbreviation for Extraverted Judging—TJ stands for Extraverted Thinking and FJ stands for Extraverted Feeling.
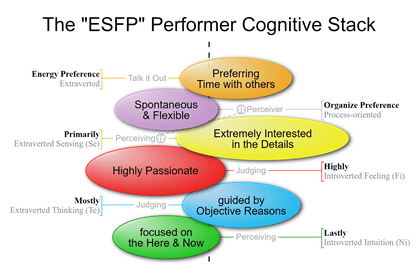
The TPs and FPs, on the other hand, are the eight MBTI types that prefer to extravert their Perceiving function. Basically, P stands for, extraverted perception.
P types prefer to use Sensing or Intuition when dealing with the world. As a result, their Judging function tends to be introverted.
In particular, TPs tend to introvert their Thinking, and FPs tend to introvert their Feeling. Thus, P also stands for introverted Judging, TP for introverted Thinking, and FP for introverted Feeling.
The Judging (J) Personality Types
Characteristics:
- You like structure.
- You like to make plans.
- You like closure.
FJs, who extravert Feelings, are the most empathetic types. FJs tend to project inwardly more than the other types other people’s values, standards, and concerns. Meaning they tend to experience those values as though they were their own, and they judge their actions and character based on those internalized values.
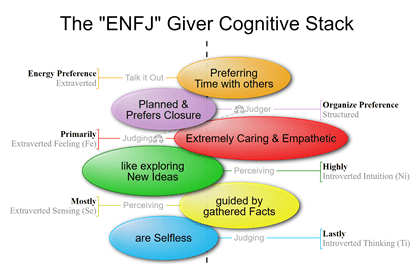
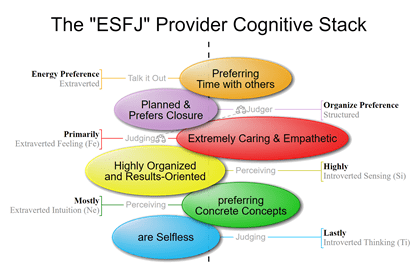
ENFJ and ESFJ-type people are Judgers because Extraverted Feeling is their Dominant Function.
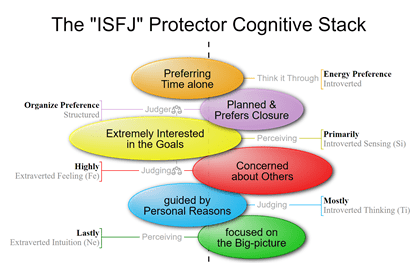
INFJ and ISFJ-type people are Judgers because Feeling is their top Extraverted Function.
TJs, with Extraverted Thinking, are the most directive types. More than the other types, they tend to project their values, standards, and concerns outwardly into others. They experience those values as though they belong to other people, and they judge the actions and character of others based on their own externalized values.
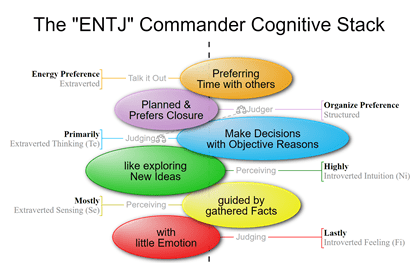
ENTJ and ESTJ-type people are Judgers because Extraverted Thinking is their Dominant Function.
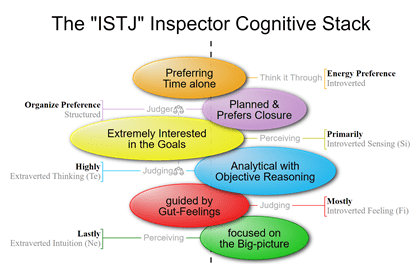
INTJ and ISTJ-type people are Judgers because Thinking is their top Extraverted Function.
The Perceiving (P) Personality Types
Characteristics:
- You are Process-oriented.
- You like to be spontaneous.
- You remain flexible.
ESFP and ESTP-type people are Perceivers because Extraverted Sensing is their Dominant Function.
ISFP and ISTP-type people are Perceivers because Sensing is their top Extraverted Function.
ENFP and ENTP-type people are Perceivers because Extraverted Intuition is their Dominant Function.
INFP and INTP-type people are Perceivers because Intuition is their top Extraverted Function.
TPs with Introverted Thinking will share their opinions and ideas, but they tend to do so in a less emotional way. Emotions are usually the last thing TPs will share with you. When they do, they tend to be more explosive and come after a period of stuffing or gunny-sacking their feelings.
TPs are the type most unlike FJs in this respect. Myers and McCaulley recognize this fundamental difference when they refer to TPs as “impersonal” and FJs as “expressive.”
While TJs are most likely to be directive and control-minded and FPs least likely, most FJs and TPs are likely to be somewhere in the middle.
Similarly, FPs with Introverted Feelings will talk about values and concerns, but they tend to do so more indirectly and less logically or critically than others. They tend to stuff their criticisms and are the type most unlike TJs in this respect.
Again, Myers and McCaulley allude to this fundamental difference in calling FPs “gentle” and TJs “tough-minded.”
And while FJs are most likely to be empathetic and ethical-minded and TPs least likely, most TJs and FPs are probably somewhere in between.
Decoding the MBTI Four Letters
The four-letter Myers-Briggs Type indicators are mnemonic codes or dichotomies for the 16 Personality Types. Each of the four letters has a specific meaning, as shown below:

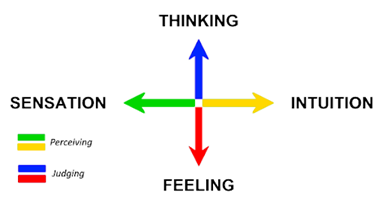
You can imagine perception and judging functions as points on a compass.
Where the Judging values of Thinking and Feeling are the North and South poles (the Judging axis), and the Perceiving values of Intuition and Sensing (Sensation) are the East and West poles (the Perceiving axis).
Each axis works as opposite pairs, so when one value is Introverted, the other must be Extraverted. For example, if Intuition on the perception axis is introverted, then Sensing must be extraverted, and vice versa.
Similarly, for the Judging pair (the Judging axis), if Thinking is Introverted, then Feeling must be Extraverted, and vice versa. Also, if the Perceiving value is Introverted, Judging must be Extraverted and vice-versa.
The following will show you how to decode the MBTI four-letter code.
1. First, let’s review the second and third letters:
- The second letter is the Perceiving value, either S (Sensing) or N (iNtuition).
- The third letter is the Judging value, either T (Thinking) or F (Feeling).
- The combinatios are: ST, SF, NT, and NF.
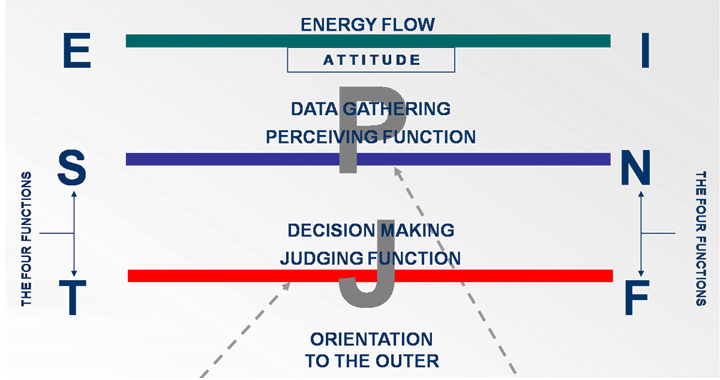
2. Next, the fourth letter is either P (if the Perceiving Function is Extraverted) or it is J (if the Judging Function is Extraverted):
- So, in other words, if the second letter is Ne (Extraverted Intuition) or Se (Extraverted Sensing), the fourth letter will be P because the Perceiving axis is Extraverted.
- Otherwise, if the third letter is Te (Extraverted Thinking) or Fe (Extraverted Feeling), the fourth letter will be J because the Judging axis is Extraverted.
3. Now, if the first letter is E (Extraversion) this indicates a Perceiving function is the Dominant (top) function; otherwise if I (Introversion) this indicates a Judging function is the Dominant (top) function:
- The first letter is independent of the last letter, which indicates which Perceiving or Judging value is the Extravterd function. Thus, the other will be Introverted (the polar opposite).
- The first letter will indicate which of the Perceinig of Judging values is the top Dominate function.
For example, here are the steps for decoding the INFJ Type:
- Step 1—The fourth letter in INFJ is a J means that the Judging value (the third letter) is Extraverted. In this case the third letter is F (Feeling) so, this means Extraverted Feelings, thus Fe.
- Step 2—If the third letter is Extraverted, then the second letter (the Perceiving value) must be Introverted (and vice versa). In this case the second letter is N (Intuition) so, this means Introverted Intuition, thus Ni.
- Step 3—The first letter in INFJ is an I (Introverted), so this means the N judging value must be the Dominant (top) Function.
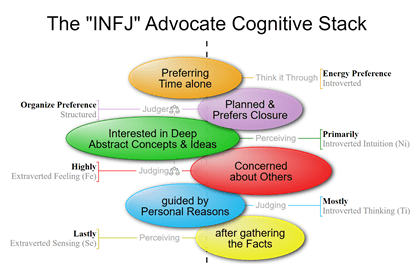
So the INFJ decoded means:
- The Dominant (first/top) function is Introverted Intuition (Ni)
- The Auxiliary (second) Function is Extraverted Feeling (Fe)
- The Tertiary (third) Function is Introverted Thinking (Ti), the opposite pole of Feeling.
- The Inferior (fourth/bottom) function is Extraverted Sensing (Se), the opposite pole to Intuition.