The Four Core Leadership Types
Leaders tend to be either Autocratic or democratic and more Task-oriented or People-oriented, forming four basic Leadership Types.
Depending on the person’s level of Assertiveness versus the level of Empathy describes their Leadership Type.
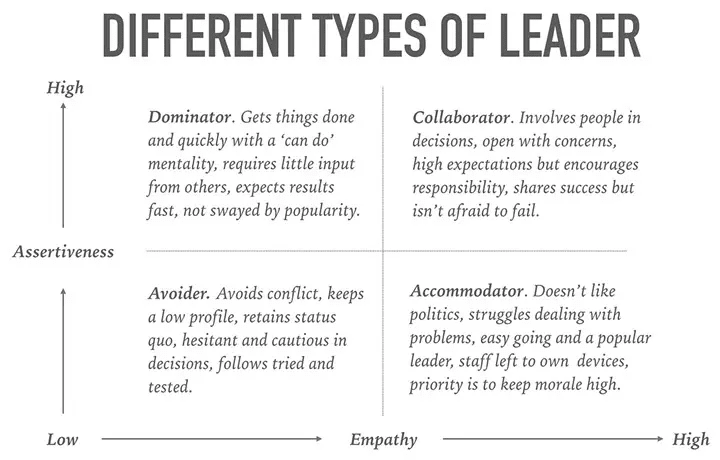
The Dominator Type
The Dominator Type is High in Assertiveness and Low in Empathy. They are Autocratic and Task-oriented in their decision-making.
Dominator Personality Type cross-reference
- Keirsey Type – Rationals
- Temperament Type – Choleric
- Animal Type – Lion
- DISC Type – Dominant
- Socio-Communicative Type – Driver
- True Colors – Green
- Color Code – Red
- Personality Compass – North
- Occupational Type – Enterprising
- Learning Type – Activist
The Collaborator Type
The Collaborator Type is High in Assertiveness and Empathy. They are Autocratic and Emotional in their decision-making.
Collaborator Personality Type cross-reference
- Keirsey Type – Idealists
- Temperament Type – Phlegmatic
- Animal Type – Otter
- DISC Type – Influential
- Socio-Communicative Type – Expressive
- True Colors – Blue
- Color Code – Blue
- Personality Compass – West
- Occupational Type – Artistic
- Learning Type – Theorist
The Avoider Type
The Advoider Type is Low in Assertiveness and Empathy. They are Democratic and Task-oriented in their decision-making.
Avoider Personality Type cross-reference
- Keirsey Type – Guardian
- Temperament Type – Melancholy
- Animal Type – Beaver
- DISC Type – Compliant
- Socio-Communicative Type – Analytical
- True Colors – Gold
- Color Code – White
- Personality Compass – East
- Occupational Type – Realistic
- Learning Type – Pragmatist
The Accommodator Type
The Accommodator Types are Low in Assertiveness and High in Empathy. They are Democratic and Emotional in their decision-making.
Accommodator Personality Type cross-reference
- Keirsey Type – Artisans
- Temperament Type – Sanguine
- Animal Type – Golden Retriever
- DISC Type – Steadiness
- Socio-Communicative Type – Amiable
- True Colors – Orange
- Color Code – Yellow
- Personality Compass – South
- Occupational Type – Conventional
- Learning Type – Reflector

The Autocratic Leadership Style

In Autocratic leadership, the leader holds authority and responsibility. They reach a decision, communicate it to subordinates, and expect prompt implementation.
This style is used when leaders tell their employees what they want to be done and how they want it accomplished without getting the advice of their followers.
Some appropriate conditions for using this style are when you have all the information to solve the problem, you are short on time, and your employees are well motivated.
Some think of this style as a vehicle for yelling, using demeaning language, and leading with threats. This is not the authoritarian style. Instead, it is an abusive, unprofessional style called “bossing people around.”
Autocratic leaders have been around for a long time in the shape of tyrants, dictators, monarchs, etc. The authoritarian style is not defined as interchangeable, i.e., a leader is either an autocratic leader, a democratic leader, or a laissez-faire leader, with no switching between styles depending on the situation. It is simply the personality of the leader.
Autocratic leadership provides advantages such as clarity, quick decision-making, improved crisis handling, and increased productivity in low-skilled teams, at least temporarily.
The disadvantages of autocratic leadership include a lack of empowerment, low engagement, and accountability within the team. It also adds an extreme dependency on the leader, and little happens if the leader is absent. Lastly, intimidation, punishment, and fear are common in autocratic leadership, leading to a toxic work climate.
The Democratic Leadership Style

The Democratic leader holds final responsibility and is still responsible for delegating the tasks that must be completed. However, the leader invites other team members to contribute to decision-making. This is usually used when you have part of the information and your employees have different interests.
A leader is not expected to know everything, so the Democratic leader employs knowledgeable and skilled people. Using this style is not a sign of weakness. Instead, it is a sign of strength that your employees will respect.
This not only increases job satisfaction by involving employees or team members in what’s going on, but it also helps to develop people’s skills. Employees and team members feel in control of their destinies and are motivated to work hard by more than just a financial reward.
The Democratic leader is favored because of its fairness, competence, and creativity. The Democratic leadership style provides the advantages of increased creativity, innovation, and collaboration, which helps solve complex problems, high employee engagement, and strong accountability through shared goals.
Thedownsides is that democratic leadershipcan weakenn productivity, which can drop while waiting for time-consuming decision processes, and it does not work well in low-skilled, inexperienced teams.
Laissez-Faire Leadership Style

Laissez-faire is a hands-off leadership style where team members can make all decisions. It is the opposite of the Autocratic leadership style since the team makes decisions without the leader.
The Laissez-faire, free-rein, absent, or zero leadership style can lead to the perception of disengaged leadership.
Laissez-faire leadership can work with highly skilled, capable, and self-motivated teams. They can do extraordinary when making all the decisions themselves. Team members get an abundance of creative freedom with this approach.
On the other hand, teams that lack the right maturity level can quickly fall apart, and confusion can spread, resulting in reduced productivity.
Task-Oriented Leadership Style
Task-oriented leaders are no-nonsense people who focus on the task and believe procedures are necessary to achieve the mission.
Task-oriented leaders prioritize organizing, creating guidelines, and assigning duties and are less concerned with accommodating employees.
Task-oriented leaders are technical, highly logical, and analytical and believe in a step-by-step solution to meet a specific goal. However, in informal, well-coordinated, and well-controlled situations, they become more pleasant and pay more attention to their employees’ morale.
People-Oriented Leadership Style
Relationship-motivated leaders treat all team members alike. Most leaders with this style are people-oriented, approachable, and friendly and pay attention to their group’s well-being.
Relationship-motivated leaders are concerned most with good interpersonal relationships, even to the point of letting the task suffer.
Relationship-motivated managers tend to become task-conscious as they are pressured by upper management for greater productivity.
Narcissistic Leadership Traits
A Narcissistic leader lacks Empathy and constantly criticizes others. Expect them to have difficulty understanding other points of view, relating to what people are feeling, and communicating meaningfully.
Frame what you say cautiously and clearly, and never confide in them.
- Narcissistic leaders profess company loyalty but are only really committed to their agendas.
- They pursue their interests rather than the organization’s interests.
- Their organizational decisions are highly influenced by their agendas.
- Productive Narcissists have an interrelated set of skills: foresight, systems thinking, visioning, motivating, and partnering.
- Productive narcissists tend to be over-sensitive to criticism, over-competitive, isolated, and grandiose.
- Productive narcissists have a sense of freedom to do whatever they want rather than feeling constantly constrained by circumstances.
- Productive narcissists, through their charisma, can draw people into their vision and gather many followers who follow them.
- Narcissist leadership suits companies that need people with vision and the courage to take them in new directions.
- Narcissist leadership can also cause trouble for companies by causing them to refuse to listen to their manager’s advice and warnings.
- Narcissistic leaders have difficulty forging long-term relationships because they continuously seek recognition from others to reinforce their self-worth.
- As leaders, narcissistic individuals have fantasies of power and success, an exaggerated, grandiose sense of self-importance, and little Empathy or concern for the feelings and needs of others.
- Such innate characteristics lead to exploiting and manipulating others to indulge a narcissistic leader’s desire for personal enhancement.
- They expect special favors without needing to reciprocate and oversimplify relationships and motives.
- They have highly bipolar worldviews, seeing things as either extremely good or bad and seeing others around them as loyal supporters or mortal enemies.


