What is the Keirsey INFJ “Counselor” Personality Type?
The Keirsey INFJ “Counselor” Personality Type is an Idealist Temperament with an Abstract Communication Style and a Cooperative Action Style.
Keirsey organized the Four Temperaments as a matrix. There are two communication styles, abstract and Concrete, similar to the Myers-Briggs Intuition (Abstract) and Sensing (Concrete) “Perceiving” Cognitive Functions.
And by two action styles: Cooperative and Utilitarian. Utilitarian people, for the most part, do what works, while Cooperative people do what’s right.
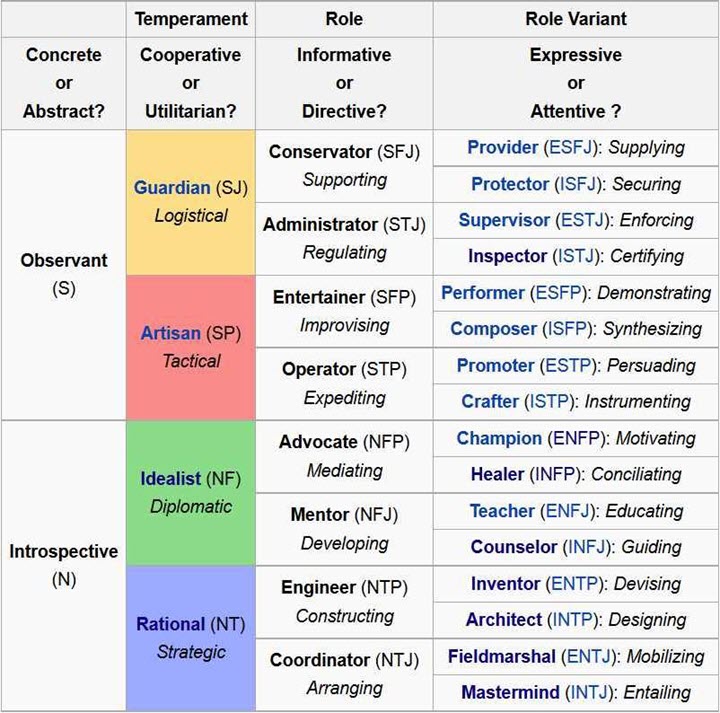
Keirsey named the Four Temperaments as suggested by Plato: Artisan (Iconic), Guardian (Pistic), Idealist (Noetic), and Rational (Dianoetic).
Concrete versus Abstract Communication Style
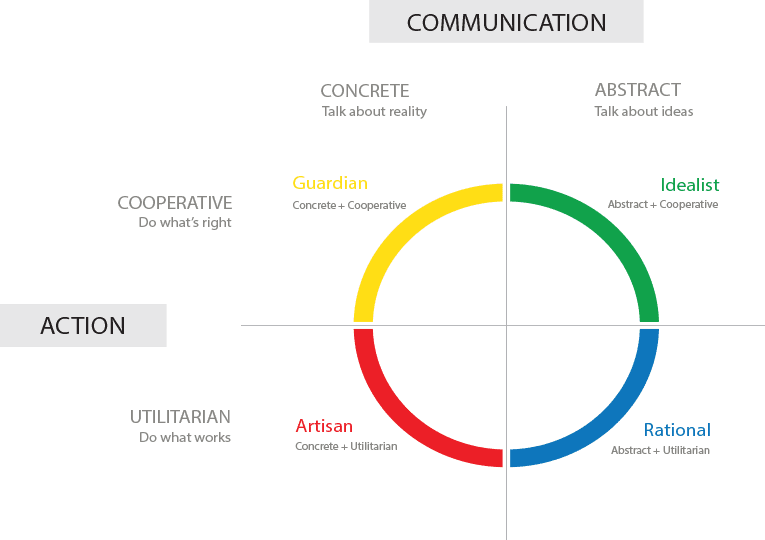
Keirsey divided the Four Temperaments into two Communication Styles: Abstract and Concrete. These styles resemble the Myers-Briggs Intuition and Sensing “Perceiving” Cognitive Functions.
Some people talk primarily about everyday reality’s external, concrete world: facts and figures, work and play, home and family, news, sports, and weather—all the who, what, when, where, and how of life.
Other people talk primarily about the internal, abstract world of ideas: theories and conjectures, dreams and philosophies, beliefs and fantasies—all the whys, ifs, and what might be of life.
Concrete people talk about reality in their daily lives, while Abstract people talk about ideas.
According to Keirsey, everyone can engage in both observation and introspection. People are observant when they touch objects or otherwise perceive the world through their five senses.
When people reflect and focus on their internal world, they are introspective. However, individuals cannot engage in observation and introspection simultaneously. The extent to which people are more observant or reflective affects their behavior.
People who are generally observant are more ‘down to earth.’ They are more concrete in their worldview and focus on practical matters such as food, shelter, and their immediate relationships. Carl Jung used the word sensation when describing people who prefer concrete perception.
Generally, reflective people have more ‘heads in the clouds’ and abstract worldviews. They focus on global or theoretical issues such as equality or engineering. Carl Jung used the word intuition to describe people who prefer abstract perception.
Cooperative versus Utilitarian Action Style
Some people act primarily practically or pragmatically; that is, they do what gets results, what achieves their objectives as effectively or efficiently as possible. They only check afterward to see if they observe the rules or go through the proper channels.
Other people act primarily cooperatively or socially acceptable; they try to do the right thing in keeping with agreed-upon social rules, conventions, and codes of conduct. Only later do they concern themselves with the effectiveness of their actions.
These two ways of acting can overlap, but as they lead their lives, Utilitarian people mostly do what works, while Cooperative people do what’s right.
Keirsey compares the differing temperaments with cooperative (Complying) and pragmatic (Adaptive) temperaments. Cooperative people pay more attention to other people’s opinions and are more concerned with doing the right thing. Sensible people (Utilitarian) pay more attention to their thoughts or feelings and are more concerned with doing what works. No comparable idea in the MBTI or Jung corresponds to this dichotomy, which is a significant difference between Keirsey’s work and Myers and Jung’s.
The pragmatic temperaments are Rational (pragmatic and abstract) and artisan (Pragmatic and concrete). The Cooperative Temperaments are Idealists (Cooperative and Abstract) and Guardians (Cooperative and Concrete). Neither the MBTI nor Jung included the concept of Temperament in their work.
INFJ Keirsey/MBTI Correlation
| Keirsey | MBTI | |
|---|---|---|
| I | Attentive Role Variant | Introverted Intuition |
| N | Abstract Communication Style | Introverted iNtuition Dominate Function |
| F | Cooperative Action Style | Auxiliary Extraverted Feeling Function |
| J | Directive Role | Feeling is a Judging Function |
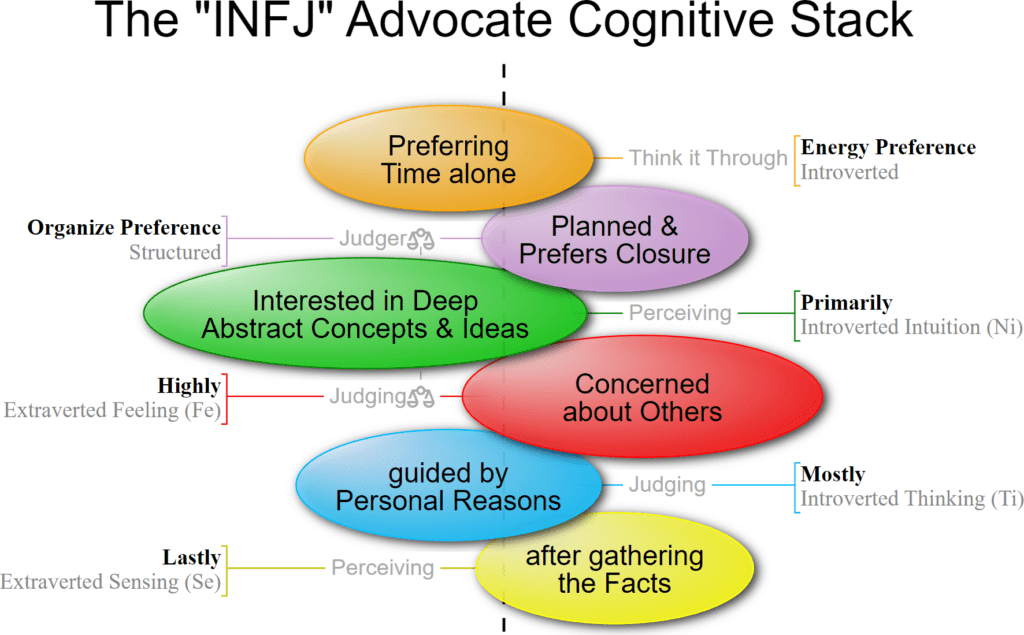
With Introverted Intuition as the first Dominant Function and Extraverted Thinking as the second Auxiliary Function, the MBTI INFJ “Advocate” Personality Type is similar to the Keirsey INFJ “Counselor” Personality Type.
INFJ Personality Type cross-reference
- Keisey Type – Counselor
- Temperament Type – Phlegmatic
- Animal Type – Otter
- DISC Type – Influential
- Socio-Communicative Type – Expressive
- True Colors – Blue
- Color Code – Blue
- Personality Compass – West
- Occupational Type – Artistic
- Learning Type – Theorist
- Leadership Type – Collaborator
Enneagram Types
Counselor Personality Characteristics
Counselors have a powerful desire to contribute to the welfare of others and find great personal fulfillment in interacting with people, nurturing their personal development, and guiding them to realize their human potential.
Although they are happy working at jobs (such as writing) that require solitude and close attention, Counselors do pretty well with individuals or groups of people, provided that the personal interactions are not superficial and that they find some quiet, private time now and then to recharge their batteries.
Counselors are kind and cheerful when dealing with others. They are great listeners and naturally interested in helping people with their problems.
Not usually visible leaders, Counselors prefer to work intensely with those close to them, especially on a one-to-one basis, quietly exerting their influence behind the scenes.
Counselors are scarce, little more than one percent of the population, and can be hard to get to know since they tend not to share their innermost thoughts or powerful emotional reactions except with their loved ones.
They are highly private people with a vibrant, complicated inner life. Friends or colleagues who have known them for years may find surprising sides emerging.
Counselors are not flighty or scattered; they value their integrity greatly, but they have mysterious, intricately woven personalities that sometimes puzzle even them.
Counselors tend to work effectively in organizations.
They value staff harmony and try to help an organization run smoothly and pleasantly.
They understand and use human systems creatively and are good at consulting and cooperating with others.
As employees or employers, Counselors are concerned with people’s feelings and can act as a barometer of the emotions within the organization.
Blessed with vivid imaginations, counselors are the most poetic of all the types, and in fact, they use a lot of poetic imagery in their everyday language.
Counselors are highly intuitive and can recognize another person’s emotions or intentions—good or evil—even before that person is aware of them.
Counselors can seldom tell how they came to read others’ feelings so keenly.
This extreme sensitivity to others could explain the Counselor’s remarkable ability to experience various psychic phenomena.
Famous Counselors
Mohandas Gandhi, Sidney Poitier, Eleanor Roosevelt, Jane Goodall, Emily Bronte, Sir Alec Guiness, Carl Jung, Mary Baker Eddy, and Queen Noor are examples of Counselor Idealists.

What are the Keirsy Personality Temerpaments?

David Keirsey, born in 1921, was an American psychologist specializing in conflict management and family counseling. He began researching human behavior and Personality in the 1940s.
Keirsey blended the Myers-Briggs Personality Types with Ernst Kretschmer’s model of the Four Temperaments, developing the Keirsey Temperament Sorter, which was made famous by his book “Please Understand Me.”
Instead of using the term Personality, Keirsey used Temperament. He viewed it as a configuration of observable Personality Traits, communication habits, patterns of action, characteristic attitudes, values, and talents. To Keirsy, Temperament encompasses personal needs, individual contributions, workplace contributions, and societal roles.
Keirsey correlated the sixteen MBTI Personality Types into Four Temperaments. He divided each Temperament into two Roles: informative and Directive. He subdivided the roles into expressive (extraverted) and attentive (introverted) role Variables.
Informative versus Directive Roles
Keirsey distinguishes between people who generally communicate by informing others versus those who speak by directing others. This distinction subdivides each of the four Temperaments into eight Roles.
Expressive versus Attentive Role Variants
Individuals who act before observing are Expressive. In contrast, people who follow before working are Attentive.
Expressive and attentive variants further subdivide the eight roles into 16 types correlating to the 16 Myers-Briggs personality types.